The population is a very important resource of a country as the development of the country is largely dependent on the quality of human resources.
Like other resources human resources are also not equally distributed over the earth; as per estimate, about 90 percent of the world's population lives in 10 percent of the land area of the earth.
Let us first analyze the historical Growth trends of the world population. The following table shows the growth trends of the world population in the past as per demographic yearbook data for 2009-10.
Population
|
Period
|
Time in which Population Doubles
|
5 million | 10,000 BC | |
500 million
|
1650 AD
|
1500 Years
|
1 Billion
|
1804 AD | 154 Years |
2 billion
|
1927 A.D.
|
123 years
|
4 Billion
|
1974 A. D.
|
47 Years
|
8 Billion
|
2025 A.D projected
|
51 Years
|
Colonization period:
During this period, there was high population growth in European countries. There was a stable population in Asia, Africa, and South America because of the high birth and high death rate.
Industrial development and Favorable food supply in Europe and North America leads to high population growth and the rest of the world were a steady or stable population.
In this period, there was a very high population growth rate due to the improvement in health facilities in the world as there was a sharp decline in the death rate during this period.
Present day, the population growth rate is actually declined due to improvment in health and education facilities, however, net population addition is very high due to the large population base.
Present day, the population growth rate is actually declined due to improvment in health and education facilities, however, net population addition is very high due to the large population base.
Present Growth Trends of World Population
The growth rate of the population of the countries is not the same; the population growth rate of the region is largely determined by geography and socio-economic factors. As per the estimate, the total fertility rate in developed countries normally varies from one to three children per woman whereas in developing countries total fertility rate varies from two to seven children per woman. That is why the growth of the world's population is seen mostly in developing countries.
Population growth
In the Asia region, the growth rate of
West Asia is 1.9%
South Asia is a 1.7%
Southeast Asia is 0.9 %
East Asia: 0.9 %
As of now ( 01-01-2023), the following are the ten most populous countries in the world in decreasing order of population:
- China ( Most populous)
- India ( Second most populous country in the world)
- The U.S.A
- Indonesia
- Brazil
- Pakistan
- Nigeria
- Bangladesh
- Russia
- Mexico
Distribution of world Population:
As per the world population report as of 26-10-2018, the region-wise population density and world share of the population are as follows:
- Asia ( Population density: 146, world population share: 59.5 %)
- Africa ( Population density: 43, world population share: 16.9 %)
- Europe ( Population density: 34, world population share: 9.7 %)
- Latin America and the Caribbean ( Population density: 32, world population share: 8.5 %)
- North America ( Population density 20, world population share:4.8 %
- Oceania ( Population density: 5, world population share: 0.5 %)
Factors affecting the population growth:
There are two major factors that affect the population growth and population density of a region:
- Physical factor or Geographical factor
- Socio-economic or human-induced factors
Climate, soils, water availability, topography, mineral resources, and other natural resources are important deciding geographical factors for the growth of the population. For example, the Indo-Gangetic plain is highly populated due to its favorable climate, fertile soil, plain areas, and abundance of water availability.
Socio-economic factors like economic opportunities, availability of infrastructure, literacy rate, health facilities, political stability, religious importance, and others are important factor that influences the growth of the population.
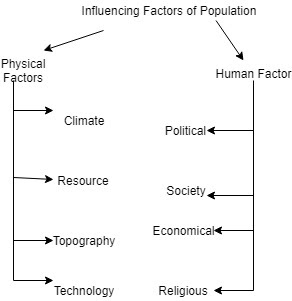 |
| influencing factors of population |
Previous years' questions asked in UPSC mains paper.
- Trace and account for the various trends of population growth in the world during the present century. (1991, 15 marks)
- Similarities in the population distribution of southern continents and reasons for the same. (2012, 12 marks)
- Impact of changing fertility ratio on world population distribution. (2012, 20 marks)



ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon