What are the organisms?
Any living entity called organisms. For examples:- Plants
- Animal
- Microorganisms
- Human
- Fungi
- Bacterias
How the balance of nature maintains?
All organism interacts with each other and with their physical environment, and maintain the balance in nature.What is an Ecosystem?
All the organisms interacting with biotic parts and non-biotic parts of particular areas form an ecosystem.What are the components of the ecosystem?
There are three components of an ecosystem:- Biotic components or living organism such as:
- Plants
- Animal
- Microorganisms, fungi, bacterias
- Abiotic Components of physical components such as:
- Soil
- Minerals
- Temperature
- Rainfall or water
- Winds or air
- Interaction
- The energy flow from one component to other components
- The interdependence of the organism
The following are examples of ecosystems:
- Gardens and crops are examples of artificial ecosystems.
- Forest, Ponds, Lakes, Ocean are an example of a natural ecosystem
What are the types of Organisms? or how the organism can be grouped together?
Based on the energy interaction, the organism can be grouped into three parts:- Producer or Autotrophs:
- The organism( i.e plants and some bacteria) can make organic components like Sugar and Starch from inorganic substances( i.e Co2, water, and minerals) using radiant energy from the Sun in the presence of Chlorophyll
- Consumer or Heterotrophs:
- The organism which can not produce energy from inorganic substance and consume food made by the producer.
- Further consumers are divided into:
- Herbivores: The consumer that only eats plants and plants products, for example, Cow and Goat
- Carnivores: The consumer that eats only animal and animal products, for example, Lion and Tiger
- Ominivorces: The consumer that eats both animal and plants products, for example, Human and Dog
- Microorganism comprised of Fungi and Bacteria:
- Eats dead plants and animals. It breakdown the dead remains and waste product of complex organic substances into simple inorganic substances.
What is the Trophic level?
Each step or level of the food chain forms a trophic level.- Autotrophs or Producers:
- First(1st) Trophic level
- Herbivores or primary consumer:
- A second (2nd) Trophic level
- Small carnivores or secondary consumer:
- Third(3rd) Trophic level
- Large carnivores or Tertiary consumer:
- Fourth (4th) Trophic level
How energy flow in the ecosystem?
- In the ecosystem, energy flow is uni-directional starting from the producer(autotrophs) to the consumer (Heterotrophs) at the different trophic levels.
- Energy does not revert back to a lower trophic level
- 90 % energy loss rule applies in each trophic level
- Green plants in the terrestrial ecosystem capture 1% of energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical energy.
- 90% of the energy generated by autotrophs goes to :
- Digestion
- Doing work
- Growth and reproduction
- 10 % of food made are available for the next level for the consumer.
- This 90 % consumption and 10 % of food Availablity happen at each trophic level.
What is food Chains?
A series of organisms feeding on one another at various biotic levels form a food chain.What is the food web?
Each organism is generally eaten by two or more other kinds of organisms. So stead of a straight line of the food chain, the relationship can be shown as a series of branching lines called a food web.What is Bio-accumulation?
Unknowingly, some harmful chemicals enter at the trophic level( it can be any trophic level from autotrophs to secondary consumers). This chemical is non-degradable in nature and gets accumulated in the organism's body, which is called bio-accumulation.What is Bio-Magnification?
This bio-accumulation gets an increase when we go up at trophic levels. It is happening because higher trophic level organisms eat the bio-accumulated bodies of lower trophic levels. This phenomenon is called bio-magnification.Trophic level 4 or secondary consumer has the highest concentration of the chemical.
Foodgrains such as wheat, rice, vegetables, fruits, fishes, and animal products contain varying amounts of pesticide residues. They can not always be removed by washing or other means.
How do our activities affect the environment?
- Our activities affect the environment through pollution such as:
- Air pollution
- Water pollution
- Soil pollution
- Our activities also affect the environment through resources depletion such as:
- Groundwater depletion
- Mineral depletion
- Forest depletion
- Land degradation
- Ozone Layer Depletion
Ozone layer depletion:
- Ozone(O3) is a very harmful and deadly poison for health if found at ground level. Whereas Ozone performs a very essential function that is preventing ultraviolet radiation to reach the ground when it found in the upper level( i.e lower stratosphere) of the atmosphere.
- Ultraviolet radiation cause skin cancer in human being.
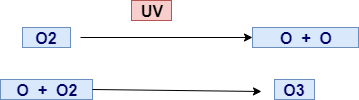 |
| Ozone formation |
- During the 1980s, the concentration of Ozone in the lower stratospheric layer was dropped due to the emission of a synthetic chemical that is CFC( Chlorofluorocarbon).
- CFC was used in:
- Refrigerator
- Fire extinguisher
- In 1987, UNEP( United Nations Environment Program) make CFC-free refrigerators throughout the world.
What is bio-degradable waste?
Substances that are broken down by biological processes or rotten down by microorganisms such as fungi are called to be bio-degradable. For examples, Kitchen garbage like Tea Leaves, vegetable waste, etcWhat is Non-biodegradable waste?
The substances that are broken down by biological processes or rotten down by microorganisms such as fungi are called to be Non-biodegradable waste. For example, Plastic waste. These types of waste persist in the environment for a very long time and harm the environment and ecosystem.
ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon