Geographer Boudeville gave the regional characteristics of the growth Poles of Perroux. As Perroux considered the growth poles as economic space, however, Boudeville considered growth poles as geographical spaces of urban areas where prominent or propulsive industries are located.
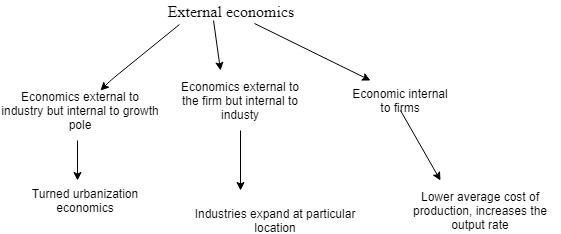 |
| external economics types |
- Economic internal to the firm
- Economic external to the firm and internal to the industry
- Economic external to the industry but internal to an urban area
Economic internal to the firm:
Advancement and innovation of single firms help to cut the price. For example, the automation of packaging in Walmart will help the internal firms.
Economic external to the firm and internal to the industry.:
This is the localization of industry. If the expansion of industry happens in a particular location, production will increase, as a result, cost per unit will decrease.
Economic external to the industry but internal to an urban area.:
For example, the development of the labor market. It Will help to expand the urbanization process and growth poles.
You may like also:
- Growth pole theory of Boudeville
- R.P Mishra's theory of regional planning
- Growth centers and growth poles
- Growth pole theory by Perroux
- SYSTEM ANALYSIS IN GEOGRAPHY
- MALTHUSIAN THEORY OF POPULATION
- MARXIST THEORY ON POPULATION GROWTH
- DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITION THEORY
- CENTRAL PLACE THEORY BY CHRISTALLER
- DIFFERENCE BETWEEN CHRISTALLER AND LOSCH ON CENTRAL PLACE THEORY
- GROWTH POLE THEORY BY PERROUX AND BOUDEVILLE
- VON THUNEN MODEL OF AGRICULTURE
- WEBER'S MODEL OF INDUSTRIAL LOCATION
- ROSTOW'S STAGES OF GROWTH IN GEOGRAPHY
- BOUNDARY AND FRONTIER IN GEOGRAPHY
- Heartland theory of Mackinder
- Rimland theory of Spykman
ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon