Table of Contents:
- Evolution of Himalayan river
- Characteristics of Himalayan river
- Indus river and its tributaries
- Ganga River and its tributaries
- Brahmaputra river and its tributaries
Evaluation of Himalayan drainage
There are differences of opinion about the evolution of the Himalayan rivers.Around, 5 to 25 million years ago, there was the largest river called Shiwalik or Indo Brahma river stretch from Assam to Punjab, and water discharged into the gulf of Sindh.
Due to Pleistocene upheaval in western Himalayan and Potwar Plateau ( Delhi ridge) and Malda gap or fault between Rajamahal hills and Meghalayan plateau; Shiwalik river got divided into three river systems:
- Indus Drainage System
- Ganga Drainage System
- The Brahmaputra Drainage System
The following are Characteristics:
- Water fed by melting of snow and precipitation
- The river is perennial in nature
- Antecedental in nature
- Deep gorge due to both erosion and upliftment at the same time.
- V-shaped valley and waterfall in their mountainous regions.
- While entering the plain, they formed deposition features:
- Flat valleys
- Oxbow lake
- Flood plain
- Delta
- Braided channel
- Strong meandering tendency and high erosion in the upper course of the river get choked in the lower course with boulders and frequent Change of river course can be seen.
- Examples, Kosi river.
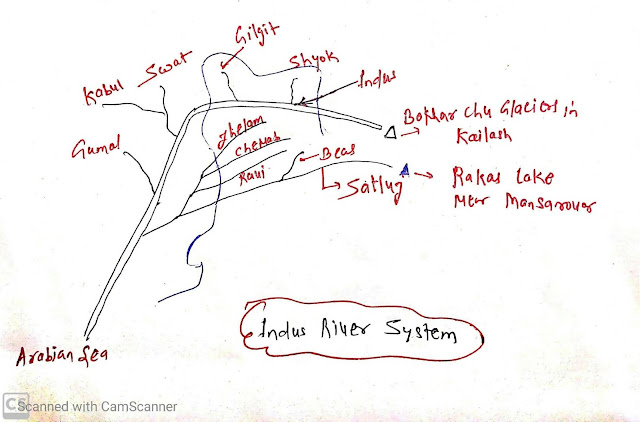
Indus River System:
- It is one of the largest river basins in the world.
- Total length 2,880 km ( 1114 km in India)
- Originated from Bokhar Chu Glaciers in Kailash Mountain ranges.
- In Tibet, it is known as Singi Khamban or lion mouth.
- It flows between Ladakh and Zaskar range.
Tributaries:
- Left Bank tributaries
- Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas, Satluj
- Right bank:
- Shyok, Gilgit, Swat, Kabul, Gumal.
Punjab has five rivers :
- Satluj, Beas, Ravi, Chenab, Jhelum.
Satluj:
- Origin: Rakas lake near Mansarovar
- Flow 400 km parallel to Indus.
- It is an antecedent river.
Beas:
- Origin : Beas kund near Rohtang pass
- Flow-through Kullu valleys
Ravi:
- Origin: West of Rohtang pass in Kullu hills of Himachal Pradesh.
- Flow from Chamba valley of Himachal Pradesh.
Chenab:
- It is the largest tributary of Indus. It is also called Chandrabhaga as it is formed by two main tributaries Chandra and Bhaga.
Jhelum:
- Origin: foot of Pir Pajal in the southeastern part of Kashmir.
- Flow-through Srinagar and Wular lake.
- It joined the Chenab river in Pakistan.
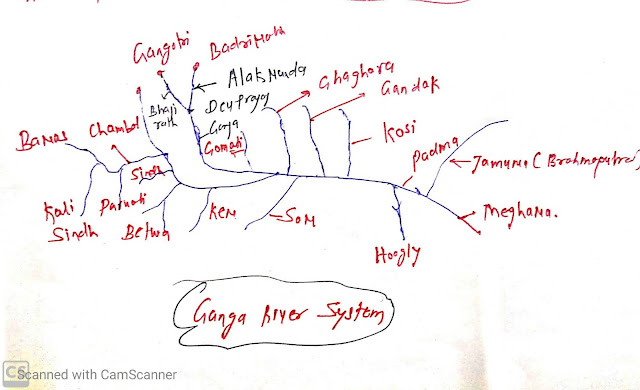
Ganga river system
Origin;
- Gangotri Glaciers near Gaumukh in Uttarkashi district of Uttarakhand, the channel is known as Bhagirathi.
- At Devprayag, Bhagirathi meets with Alaknanda and known as Ganga.
- Total Length: 2525 km.
- Uttarakhand: 110 km
- Uttar Pradesh: 1450 km
- Bihar: 445 km
- West Bengal: 520 km
- Right bank tributaries:
- Yamuna
- Son
- Damodar
- Left bank tributaries:
- Ramganga,
- Gomti,
- Ghaghara
- Gandak,
- Kosi
- Mahananda
Yamuna :
- Source: Yamunotri glaciers
- Right bank tributaries:
- Chambal,
- Sind,
- Betwa
- ken.
- Left bank:
- Hindon,
- Rind,
- Sarnar
Chambal:
- It rises near Mhow in Malwa plateau in MP.
- Chambal is famous for its badlands topography called the Chambal ravine.
Gandak:
- Comprises of two-stream:
- Kaligandak
- Triahulganga
- It rises in Nepal Himalayas be between Dhaulagiri and Mount Everest
- It join ganga near ganga.
Ghaghara:
- Originated in glaciers of Madchachunio
- Tila, Seti, and Beri tributaries, Sarda ( Kali Ganga)
- Join Ganga at Chhapra.
Kosi:
- It is an antecedent river, originated north of mount Everest in Tibet.
Ramganga:
- Origin: Garwal hills near Gairsain
- Join Ganga near Kannauj.
Damodar:
- Eastern margin of Chotanagpur plateau.
- Join tributaries of Hugali.
- Once it was the sorrow of Bengal.
Sarda or Saryu rise:
- Rises in Milan Glaciers in Nepal Himalayas, it was known Goriganga.
Mahananda:
- Origin: Darjeeling hills.
- Tributaries of Ganga
Son:
- Son is the largest south bank tributaries is Ganga.
- Origin: Amarkantak hills
- Join Ganga from the west of Patna.
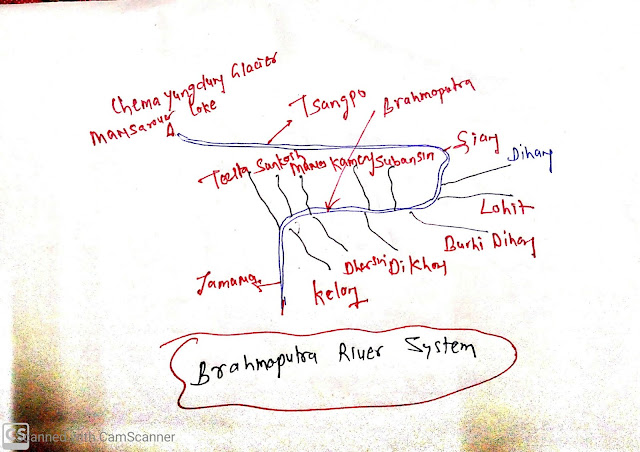
Brahmaputra River Systems
Origin:
- Chemayungdung Glacier of Kailash range near Mansarovar lake.
- In Tibet:
- It is known as Tsangpo, it is 1200 km length in Tibet.
- It enters India through Namcha Barwa and it is called Siang in Arunachal Pradesh.
- In Assam, it is called the Brahmaputra.
- In Bangladesh, it is called Jamuna.
- Left Bank tributaries:
- Dihang
- Lohit
- Burhi Dihang
- Kelong
- Right bank tributaries:
- Subansiri,
- Kameng,
- Manas
- Sankosh,
- Teesta
Subansiri:
- Antecedents river originated from Tibet.
Brahmaputra river( Jamuna) join Ganga (Padma river) in Bangladesh and discharge water in the Bay of Bengal and also make world largest delta Sundarban Delta on the mouth.


3 Comments
Click here for CommentsSir iska compile pdf milega??
ReplySir pdf kaise milega
ReplySir repli
ReplyConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon