Table of Contents:
- What is Geological
Structure?
- Geological History
of India
- Geological division
of India
- Peninsular India
- Himalayan
Mountains
- Northern Plain
- The geological timescale of India
- Geological Structure of India
- Relief of India
What is the Geological Structure?
The geological time scale of rocks means chronological dating of rocks.
Geological History of India:
- 250 million years ago, there was a supercontinent Pangeas.
- 200 million years ago, in Triassic time, Pangaea broke out into two parts; Laurasia( in the north) and Gondwanaland( in the south).
- The oldest landmass peninsula India was part of Gondwanaland land that include India, Australia, Africa, Madagascar, South America, Antarctic.
- Due to convection current, the Gondwanaland landmass breaks up into many parts of about 140 million years ago in Jurassic time.
- India and Australia got separated from Gondwanaland.
- Later It also broke out into a two-part India plate moves north and the Australia plate moves south.
- 80 Million years ago India is about 6400 km from the current position
- About 50 million years ago, Indian plates collides with Eurasian plates.
- Due to the collision of the Indian plate into Eurasian plates. Sedimentary rocks are accumulated in the geosyncline area that is Tethys sea and Himalayan mountain created on Tethys sea.
- The northern part of the peninsula subsidies under Eurasian plates and large basins are created. Over time it gradually filled by river sediments and great northern Indian plain developed.
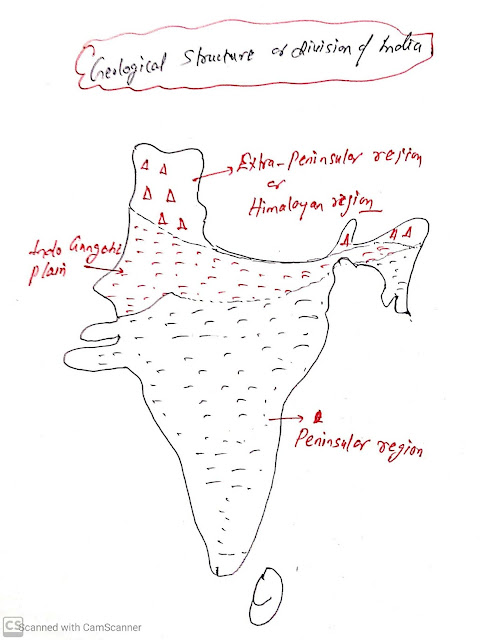
Geological Division of India:
On the basis of geological history, there is three-part of India:
- Peninsular plateau( Pre-Cambrian Period; 4000 million to 541 million)
- Himalayan range( Tertiary Period; after Extinction of Dinosaur; less than 50 million years old.)
- Northern Indian Plain ( quaternary Period)
Northern Indian plains:
- It is formed by sedimentary deposits of alluvial soil that is deposited by the Himalayan drainage system.
- It lies between the Himalayan in the north and peninsular India in the south.
Himalayan:
- It is formed by metamorphics and sedimentary ricks.
- We will discuss the relief feature of the Himalayan structure in the physiographic division of India's article.





1 Comments:
Click here for CommentsIndia relief note plz sir
ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon