Table of Contents
- Evaluation of Peninsular drainage system
- East Flowing river
- West flowing river
The peninsular drainage system is older than the Himalayan drainage system as the peninsular river is a largely graded shallow valley.
Evolution of peninsular drainage system:
Three geological events shaped the drainage system:- Subsidence of western part of peninsular undersea in the tertiary period.
- The upheaval of the Himalayas and the northern part of peninsular subsidence.
- Tilting of the peninsular block from northwest to southeast direction leads to the flow of drainage system towards the Bay of Bengal.
- River system;
East Flowing river or river discharging in the bay of Bengal:
The following are the east-flowing river from north to south:- Damodar river
- Subarnrekha
- Brahmani
- Mahanadi river
- Godavari river
- Krishna river
- Penner
- Polar
- Ponnaiyar
- Cauvery river
- Vaigai
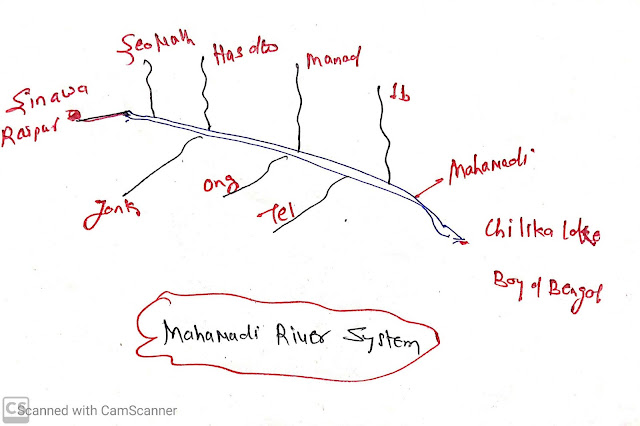
Mahanadi river
- Origin:
- Sinawa in Raipur district of Chhatisgarh.
- State:
- Chhatisgarh and Orissa.
- Length:
- 852 km
- Drainage basin:
- 53% in Mp and Chhatisgarh
- 47% in Orissa
- Left Bank tributaries:
- Seonath
- Hasdeo
- Monad
- IB
- Right Bank tributaries:
- Jank
- Ong
- Tel
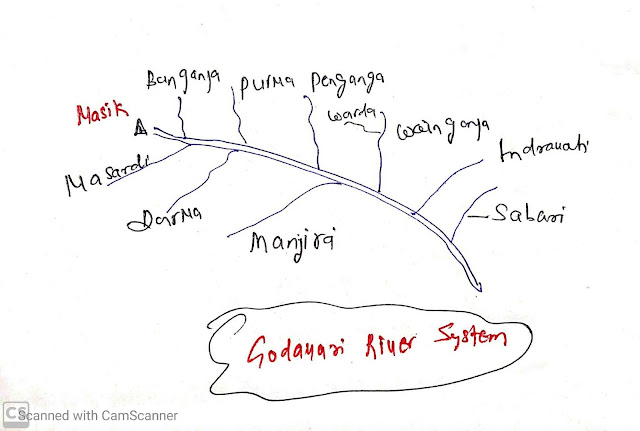
Godavari river:
- The largest river system in peninsular India.
- It is called Dakshin Ganga.
- Origin:
- Nasik district of Maharashtra.
- States:
- Maharashtra,
- Madhya Pradesh,
- Chhatisgarh,
- Odisha
- Andhra Pradesh.
- Length:
- 1465 km
- 49 % of catchment areas live in Maharashtra.
- Left bank Tributaries:
- Banganaga
- Purna
- Pen Ganga
- Warda
- Wainganga
- Indravati
- Sabari
- Right bank tributaries:
- Nardi
- Darna
- Manjira
Krishna river system:
- Second largest east-flowing river.
- Origin:
- Near Mahabaleshwar in Sahyadri.
- Length:
- 1401 km
- Catchment areas:
- 27% Maharashtra
- 44% Karnataka.
- 29% Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
- Left Bank Tributaries
- Bhima
- Dindi
- Musi
- Paleru
- Munneru
- Right Bank Tributaries:
- Koyna
- GhatPrabha
- MalPrabha
- Tungabhadra
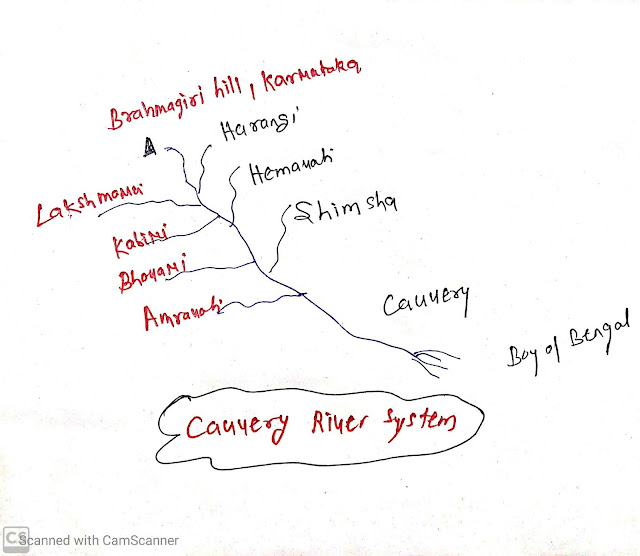
Cauvery River
- Origin:
- Brahmagiri hill in western Ghats in Karnataka.
- Length:
- 800 km
- The upper coarse of the river receives rainfall from the Southwest monsoon and the lower coarse of the river receives rainfall from the Northeast monsoon.
- Basin areas:
- 3% Kerala
- 41% Karnataka
- 56% of Tamil Nadu.
- Left bank Tributaries:
- Harangi
- Hemavati
- Shimshal
- Right Bank Tributaries:
- Lakshmana
- Kabini
- Bhavani
- Amravati
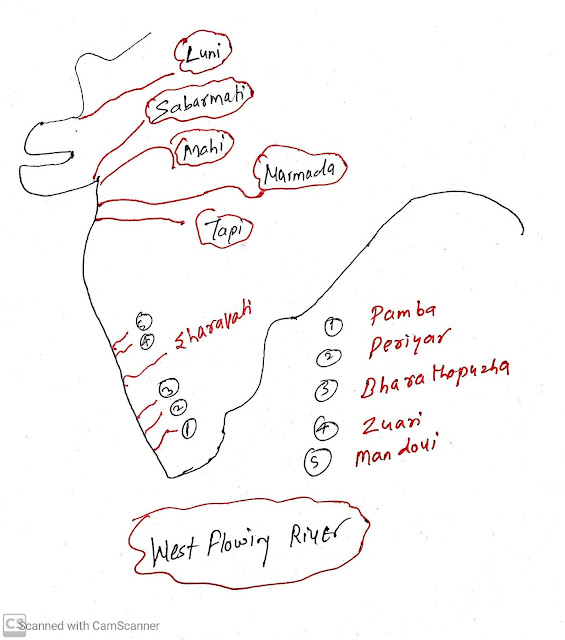
West Flowing river discharging in the Arabian sea:
The following are west-flowing rivers from north to south sequences:- Luni
- Sabarmati
- Mahi
- Narmada River
- Tapi
- Mandovi
- Zuari
- Sharavati
- Bharathapuzha
- Periyar
- Pamba
Narmada river:
- Origin:
- Rise in Amarkantak plateau
- Flow-through rift valley between Satpura in the south and Vindhya in South.
- Dhanvandhar water fall in Jabal pur.
- Length: 1312 km
Tapi river:
- Origin:
- Multai in the metal district of Madhya Pradesh.
- Length:
- 724 km
- River basin;
- 79%Maharashtra
- 15% Madhya Pradesh
- 6% Gujarat.
Luni:
- It is the largest river in the Thar desert of Rajasthan.
- The Source of the Luni river is the Pushkar valley of the Aravali range.
- Luni River is also known as "Sagarmati" river.
- Mouth of Luni river is Rann of Kachchh.




1 Comments:
Click here for CommentsThis is a good initiative. Thank you.
ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon