Table of Content:
- Purpose of Agro-Climatic zone
- What is the Agro-Climatic Zone?
- Basis of division
- 15 Climatic zones
Purpose of Agro-climatic zone division:
As we have already studied that there are some negative outcomes of the green revolution. One negative outcome was; that it increased regional disparity.
To reduce the agriculture regional disparity, In the 7th five-year plan(1985 to 1990), the planning commission of India delineated India into 15 "Agro-climatic zone". Mains' aim was to reduce the regional disparity, increase agriculture productivity, and micro-level agriculture planning.
What is Agro-Climatic Zone;
As per the Food and agriculture organization(FAO)1983, Agro-Climatic Zone is a land unit that represents the major climate and growing period precisely.
Here growing period includes Kharif, Rabi, and Zaid.
Basis of Divisions of Agro-Climatic Zones:
Both agriculture and Climatic variables are considered to make homogeneous regions for agriculture. The following variables:
- Agriculture variables:
- Growing period
- Climatic variables:
- Temperature
- Rainfall
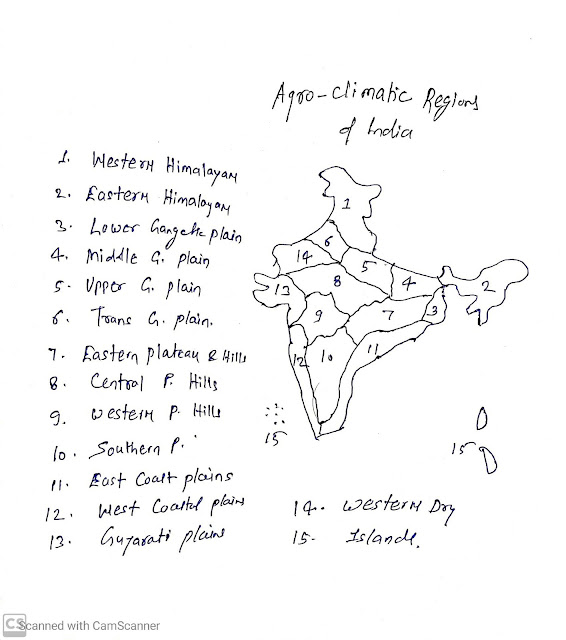
On the basis of these variables and as per the Planning commission, the following are the 15 climatic zones of India:
- Western Himalayan
- Eastern Himalayan
- Lower Gangetic Plain
- Middle Gangetic Plain
- Upper Gangetic Plain
- Trans Gangetic Plain
- Eastern Plateau and Hills
- Central Plateaus and Hills
- Western Plateau
- Southern Plateau
- Eastern Coastal Plains
- Western Coastal Plains
- Gujarat Plains
- Western Arid Plains
- Islands
Western Himalayan:
Areas:
- Jammu and Kashmir
- Ladakh
- Himachal Pradesh
- Uttarakhand except for plain areas.
Characteristics:
- Rainfall 100 to 200 cm
- The low temperature all the year
- Hilly terrain
- Major crops:
- Plantation crops; Walnut, Litchi, Almonds, Cherry
- Saffron
Eastern Himalayan:
Areas:
- All northeastern states and the Darjeeling district of West Bengal
- Characteristics:
- The highest rainfall in the world
Crops:
- Rice + fish
- Orange
- Tea
Lower Gangetic Plains:
Areas:
- West Bengal except for Darjeeling
- Eastern Bihar
Crops:
- Rice,
- Jute,
- Potato
Middle Gangetic Plains:
Areas:
- Eastern Uttar Pradesh
- Western Bihar
Crops:
- Rice
- Maize
- Wheat
Upper Gangetic Plains:
Areas:
- Central and Western Uttar Pradesh
- Plain areas of Uttarakhand
Crops:
- Rice
- Wheat
- Sugarcane
Trans Gangetic Plains:
Areas:
- Punjab, Haryana, Delhi, northern Rajasthan
Crops:
- Wheat, grams, pulse, Sugarcane, rice
Eastern Plateau and Hills:
Area:
- Chota Nagpur
Crops:
- Rice, Millet, Groundnut
Central Plateau and Hills:
Areas:
- Bundelkhand
- Bakhelkhand,
- Vindhyas
- Eastern Malwa Plateaus
Major Crops:
- Cotton, Soybeans, Pulse
Western Plateaus:
Areas:
- Western Deccan,
- Malwa Plateau
Crops:
- Cotton, Millet, Pulse
Southern Plateaus:
Areas:
- Southern Deccan,
- Maharastra,
- Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Tamil Nadu.
Crops:
- Cotton, Millet, tea, Spices
Eastern Coastal Plains:
Areas:
- Odisha, Andhra, and Tamil Nadu coast
Crops:
- Rice, Jute, Tobacco, Sugar Cane.
Western Coastal Plains:
Areas:
- Maharastra
- Karnataka, and Kerala coast
Crops:
- Rice, Coconut, and oilseeds.
Gujarat Plains:
Crops:
- Groundnut, Cotton
Western Dry Plains:
Crops:
- Mung, Bajara, Jowar
Islands:
Areas:
- Lakshadweep
- Andaman and Nicobar islands.
Crops:
- Rice, Maize, Turmeric.
1 Comments:
Click here for Commentsis it enough for mains
ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon