Law of the sea came into existence in 1982 under UNCLOS III( United Nations convention under the law of the sea) in New York. As of now in 2020, there are 168 signatories of this convection.
The Law of the sea is only international maritime law.
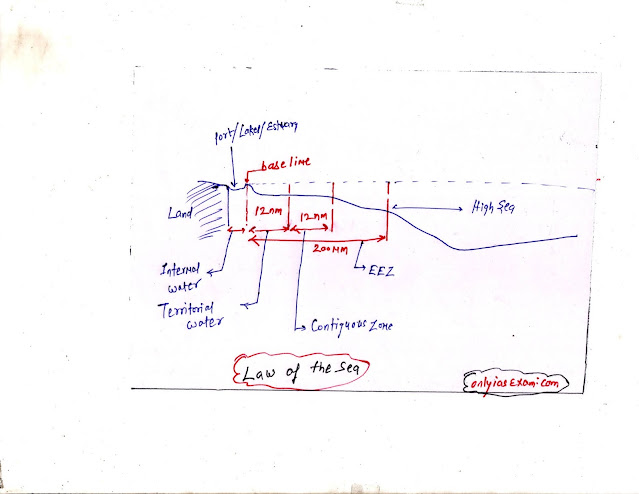
The Law of the sea divides marine areas into five zones:
- Internal Water
- Territorial water
- Contiguous zone
- Exclusive Economic Zone( EEZ) or Territorial sea
- High Sea
The different legal status is provided to the different maritime zone.
Internal Water:
- It comprises the landward side of seawater.
- It includes bays, ports, inlets, rivers, and lakes connected to the sea.
- Each coastal state has sovereign rights over internal water.
Territorial Water:
- It extends 12 nautical miles from the base level of the sea.
- The coastal state has sovereign rights over the water, air, and soil except
- the coastal state does not have the right to discharge the pollutants as it will affect the other countries also.
- Innocent people such as forced migrants can travel in these areas
Contiguous zones:
- It extends from 12 to 24 nautical miles.
- Coastal states have only right over ocean water, and ocean floor, but do not have right over air and space.
- The emigration rule applies here.
- No countries can discharge pollution here.
Exclusive economic zone( EEZ) or Territorial Sea:
- it extends from 24 to 200 nautical miles from the baseline.
- Coastal states have rights over marine resources but do not have the right to prohibit freedom of navigation.
High sea:
- It starts from 200 nautical miles from the baseline.
- It is open to all and the common heritage of all mankind.
Try to solve the following questions:
- Discuss Maritime Zones. ( UPSC 2016, 150 words, 10 Marks)


ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon