Question.
Describe the planning regions of India. ( UPPSC, 2020, 15 Marks)
Answer.
Planning regions are those areas where economic planning is implemented for the overall development of the region and it is characterized on the basis of homogeneity of physical and socio-cultural.
- For optimal developmental planning, the planning area should be small but also large enough to accommodate the availability of resources.
- Nation, state, and district are examples of planning areas of India.
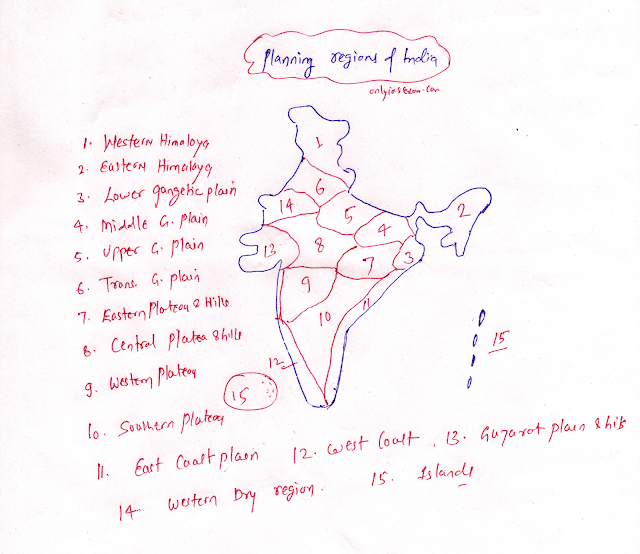
In 1965, V. Nath delineated India into 15 main and 48 sub-regions on the basis of physical factors, agricultural land use, and cropping patterns.
The following are the 15 main planning areas of India:
Western Himalayas:
Area:
- Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, and Uttarakhand.
Eastern Himalayas:
Area:
- Sikkim, hilly region of West Bengal, north-eastern state.
Lower Ganges Plain:
Area:
- Plains of West Bengal
Middle Ganges Plain:
Area:
- Eastern Uttar Pradesh, Bihar
Upper Ganges Plain:
Area:
- Southern, Eastern, and Western Uttar Pradesh.
Trans Ganga Plain:
Area:
- Delhi, Haryana, Punjab, East Rajasthan plain.
Eastern Plateau and Hills:
Area:
- Chotanagpur Plateau, Odisha
Central Plateau and Hills:
Area:
- Bundelkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Eastern Rajasthan.
Western Plateau and Hills:
Area:
- Madhya Pradesh, Malwa Plateau, Maharashtra,
Southern Plateau and Hills:
Area:
- Telangana, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu
East Coast Plain:
Area:
- Plains of Odisha, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu.
Western Coastal Plain:
Area:
- Plains of Goa, Karnataka, Kerala.
Plains and Hills of Gujarat:
Area:
- Plains of Saurashtra and hills of Gujarat
Western Dry Zone:
Area:
- The western part of Rajasthan.
Island area:
Area:
- Lakshadweep Islands, and Andaman and Nicobar.
You may like also:

ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon