Walter Penck was a German geographer, Penck gave the slope replacement model. In the process of evolution and erosion of landforms, there is a development of new slopes and replacement of slopes over time take place.
As per Penck, there are four types of slope:
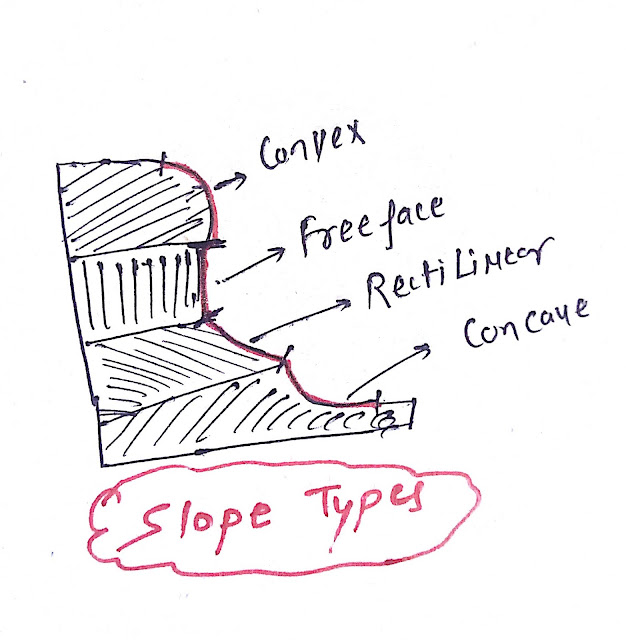
- Convex slope
- Free Face slope
- Rectilinear Slope
- Concave Slope
Convex slope:
- The feature of the terrain in which there is a slope like the outer part of the sphere is called convex slope. It develops by tectonic uplift.
Free Face slope:
- The free face is a steep wall-like slope.
Rectilinear slope:
- It is a linear gentle slope like a hill slope.
Concave slope:
- It is a terrain feature that has a slope like the interior of a circular bowl called a concave slope.
 |
| slopes types |
Slope replacement model of Penk:
As per Penck:
- Convex and free/straight slopes retreat parallel.
- The free/straight gradient retreats parallel.
- There is rapid erosion in a convex slope
- The retreating slopes (convex and free/straight) later converge together on a concave slope.
- The rectilinear slope does not have much erosion, only the eroded material is transported.
- On concave slopes, deposition of erosive material occurs.
- Later with time, the free face slope and the convex slope converge to the rectilinear slope.
- Eventually, the rectilinear slopes turn into concave slopes.
- Along with the rejuvenation of the landforms, the process of changing the slopes continues.
What is a Graded slope:
As per Penk, a Graded slope has three parts:
- Zone of erosion
- Zone of transportation
- Zone of deposition
The erosion zone includes convex and free slopes as erosion works on these slopes.
In rectilinear slope, neither erode nor depositional take place. Eroded materials from the zone of erosion are transported to a concave slope.
The zone of deposition is on a concave slope.
You may like also:
ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon