Bilateral relations between India and Bhutan:
Bilateral relations between India and Bhutan are unique, time-tested, trusted, and mutually beneficial.
The following are major characteristics of India Bhutan relations:
- Both India and Bhutan are founding members of SAARC( South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation), BBIN(Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, and Nepal), and BIMSTEC( Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and economic cooperation).
- Around 60,000 Indians are employed in hydroelectric power construction and road construction in Bhutan.
- A large number of Bhutanese students come to India to study higher education and India provides a number of scholarships to Bhutanese students.
- There is strong bonding between countries from a cultural perspective.
- India helping Bhutan in the construction of Hydro-power projects and also importing surplus electricity.
- India also provides financial support to Bhutan's five-year plan. For example, India has allocated Rs. 4500 crore to Bhutan's 12 five-year plan of Bhutan.
- India is the largest trading partner of Bhutan. India provides the duty-free transit of Bhutanese goods for export.
The following are reasons for such good relations:
Historical factors:
The following are some important treaties between India and Bhutan:
Treaty of Punakha( 1910)
- Bhutan was a protectorate state under British India since 1910 in which Britishers guide foreign affairs and defense affairs.
Friendship treaty of 1949:
- After the Independence of India, Protectorate state status was also extended based on the "Indo-Bhutan Treaty of Peace and friendship of 1949"
India-Bhutan trade and transit agreement of 1972:
- It provides the duty-free transit of Bhutanese export.
Treaty of cooperation in Hydropower and protocol of 2006:
- India is ready to help to develop a minimum of 10000 MW of hydroelectricity by 2020.
The revised treaty of the friendship of 2007:
- It revised India's role in Bhutan's external affairs as a close friend and equal partner.
Socio-cultural factors:
- Buddhism has reached Bhutan from India.
Geopolitical factors:
- Bhutan is a neighboring country of India and serves as a buffer state between India and China (Tibet).
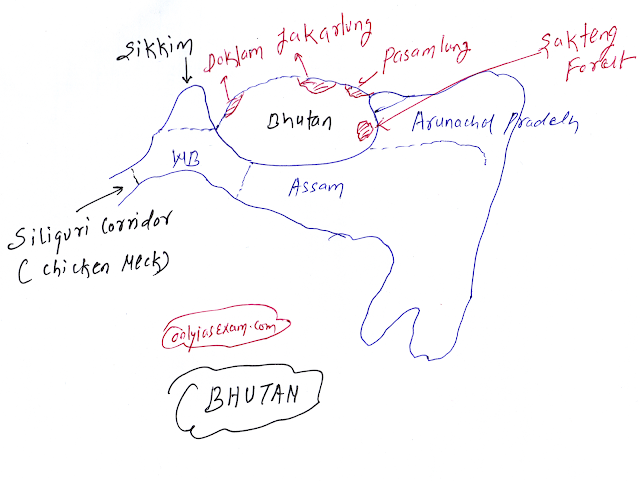
- Bhutan shares a land border of 699 km with India and the following Indian states share a border with Bhutan:
- Sikkim is in the western part of Bhutan and it shares 32 km of land border.
- West Bengal and Assam are in the southern part of Bhutan and it shares a land border of 113 km and 267 km respectively.
- Arunachal Pradesh is the eastern part of Bhutan and it shares 217 km of land border.
- India is surrounded by Bhutan on three sides and China is on the north.
- There is peaceful border management between India and Bhutan while there is a dispute between Bhutan and China on the border. Therefore Bhutan feels insecure with China, one of the reasons for its strong friendship with India.
- Bhutan's cooperation with India is much needed as it provides chicken neck and security to the northeastern state of India.
- Bhutan also played a major role in curbing anti-India activities in the northeastern states.
- Politically stable Bhutan is much needed to stop anti-India activities and anti-India extremist groups.
New geopolitical relations emerging between India and Bhutan:
- China claims its rights over Pasmalung and Jakarlung Valley (which is located in the northern part of Bhutan).
- China has also claimed a large part of the Doklam plateau. The Doklam standoff took place in 2017 between India and Bhutan.
- On June 2-3, 2020, China claimed the eastern border of Bhutan as a disputed territory and objected to the funding of the Sakteng Forest from the UNDP-led Global Environment Facility. Its purpose is to spoil the good relations between India and Bhutan.
- The biggest question mark on the relations between India and Bhutan is how to deal with China. China has proposed a package solution (land swap) for Bhutan, which has also increased India's concern.
What is needed to strengthen the bilateral relationship between India and Bhutan?
- India should refrain from interfering in Bhutan's internal affairs.
- The delay in hydropower construction by Indian companies increases the interest of Bhutan's debt, this also needs to be resolved.
- Both the countries should seek to cooperate in new dimensions of relations like space, pharma, and information technology.
Bhutan and India are natural partners and the relationship between them have multidimensional. Bhutan is not only geographically close to India but also has shared history, culture, and spiritual traditions.
Try to solve the following question:
- Discuss the geopolitical impact of the bilateral relationship between India and Bhutan. ( 10 Marks) ( UPSC 2021 geography optional)
- Bhutan India's relations are multidimensional. Discuss.
- India and Bhutan are natural partners. Discuss.
ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon