Question.
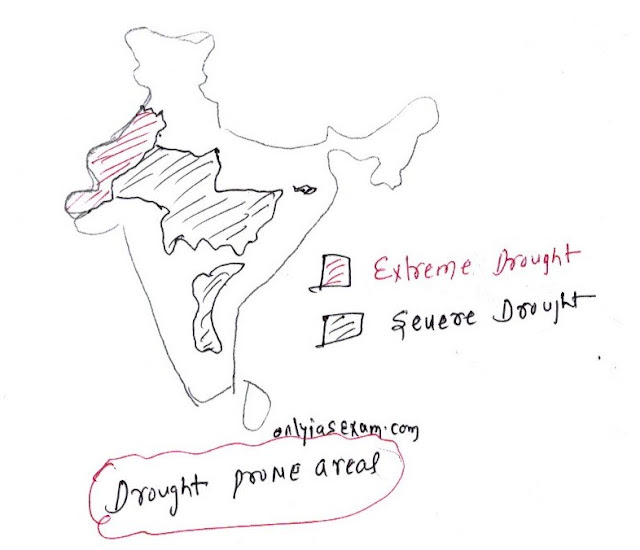
Why are there more droughts in Central and Western India?
(Chapter 7 Natural Hazards and Disasters, Class 11 NCERT geography "India Physical Environment")
Answer.
Drought is a type of hydrological disaster. Drought can be defined as a lack of availability of water over a long period of time due to insufficient rainfall, excessive rate of evaporation, and overuse of reservoirs including surface reservoirs or groundwater.
According to estimates, about 19 percent of the total geographical areas of India and 12 percent of the total population of India suffer due to drought every year.
Drought is mainly caused by the uncertainty of monsoons in India.
Central and western India are more prone to droughts such as Rajasthan (western part of Aravallis), eastern Rajasthan, most of Madhya Pradesh, the eastern part of Maharashtra, and Telangana.
The following are the reasons for more drought in western and central India:
The low rainfall and the uncertainty of monsoon rainfall are major causes of excess drought in central and western India. For example, the average rainfall in western Rajasthan is less than 90 mm. Most of central India receives less than 75 cm of rainfall.
Central and western India lack high mountains, plus they are too far from the sea, which is why monsoon winds do not bring enough rainfall. The uncertainty in monsoon rainfall in these regions is high.
Central and western India lacks groundwater levels as most of the region is either desert or highland plateaus.
Central and western India lacks a perennial river that can supply water throughout the year.
Due to all these reasons, there are more droughts in western and central India.
You may like also:
ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon