Question.
What is natural vegetation? Under what climatic conditions are tropical evergreen forests develop?
(Chapter 5 Natural Vegetation, Class 11 NCERT geography "India Physical Environment")
Answer.
Natural vegetations are those plant communities that grow naturally without human supervision. Natural vegetation adapts itself to the local climatic conditions and the soil present there.
Examples of natural vegetation are the rain forests of the Western Ghats, tropical deciduous forests of central India, mangroves of the delta region, temperate vegetation of the Himalayan region, and thorny vegetation of the desert.
Tropical evergreen forests;
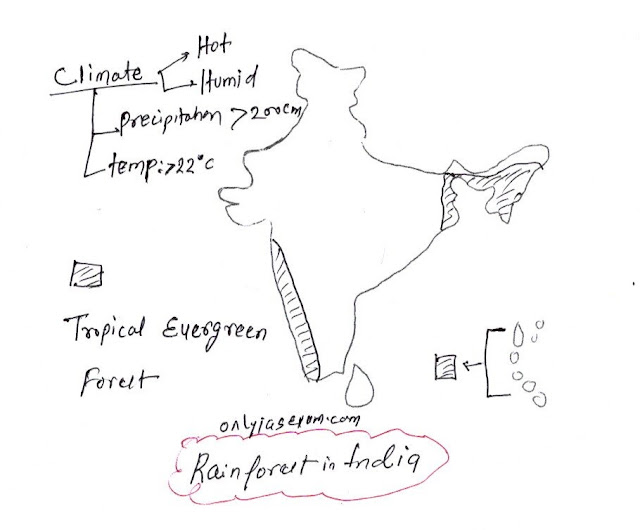
Tropical evergreen forests are also called tropical rainforests.
The climatic conditions for tropical evergreen forests are;
Tropical evergreens are found where the climate is hot and humid, such a climate is also called an equatorial climate.
The tropical rainforest climate has an annual rainfall of more than 200 cm; rainfall happens throughout the year and average annual temperatures are generally above 22 °C.
The equatorial climate is best suited for tropical evergreen forests. In equatorial climates, the high rainfall and high temperature are evenly distributed throughout the year. There is no dry season in this climate.
Area of tropical evergreen forests in India;
Tropical evergreen forests are found in the following region;
- The western slope of the Western Ghats.
- In the hills of the northeastern states.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
The important trees of tropical evergreen forests are rosewood, mahogany, cinchona, and ebony.
You may like also:
ConversionConversion EmoticonEmoticon